
Help
Users can learn about the database content through the following user manual.
1. Species information

(1) The following shows 10 apiales plants and 2 model species in the database.
Click the button to view some classification information of the species.

(1) Species information is displayed in tables. The header includes species, NCBI taxonomy ID, common name, Wikipedia link and overview respectively.
2. N6-methyladenosine(m6A)

(1) The table contains the number of m6A related genes.click number to view more information.
(2) Click CDS and Pro to download the sequence of MTA-70 genes in this species.
3. Transcription factors

(1) Click the switch button to view information related to a transcription factor in different species.
(2) Click more to view the 58 transcription factor information of this species.
(3) Click the button to download the 58 transcription factor sequences of this species.
(4) Statistical Chart of 58 Transcription factors.
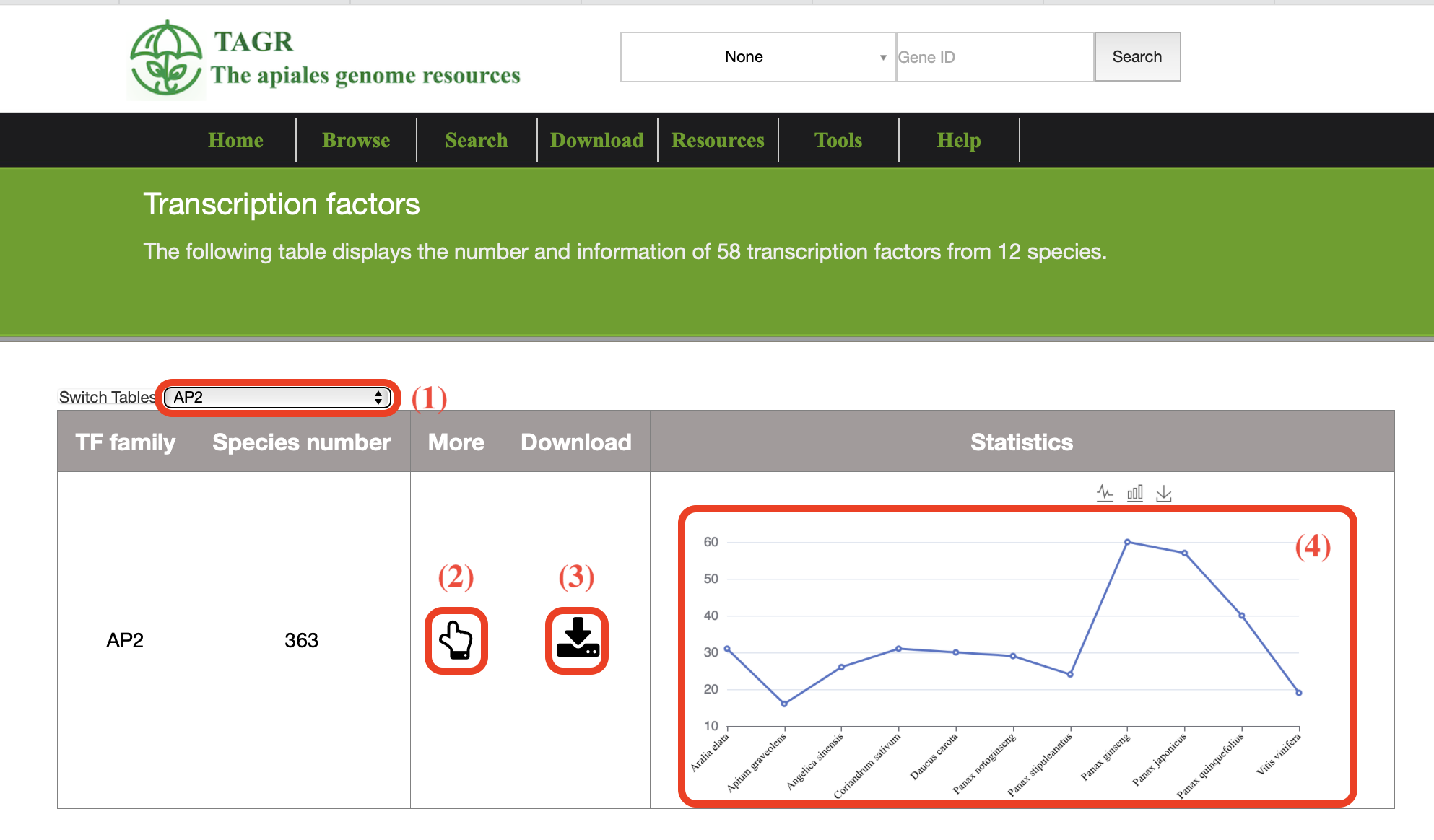
(1) Switching 58 transcription factors to view the number of different species of a transcription factor.
(2) Click more to view 12 species of this transcription factor.
(3) Click the button to download the 12 species sequences of this transcription factor.
(4) Statistical Chart of 12 species in this transcription factor.
4. Functional genes

(1) Click the download button to choose to download the CDS sequences of different functional genes.
(2) Click more to view the functional gene information of this species
(3) Statistical charts of four functional genes in this species.
1. Gene Cluster

(1)Select the species you want to view.
(2) View the gene family of the selected species.
(3) Pan-genome analysis of Solanaceae to help users view results at an overall level.
2. Synteny and rearrangements

(1) Display chromosomal structural variations.
(2) Save and Reload data.
(3) Switch between displayed samples.
(4) Click on specific segments to display detailed location information.
3. Structural variantion

(1) Select the samples and compilation types you want to view.
(2) Input chromosome numbers and start/end positions to increase query speed.
(3) View and download results.
1. Annotation

(1) Select the required search type to realize cross species search.
(2) Click the download button to download the XLS of the above search results form.

(1) Search input the gene ID, and the genome will be automatically identified laters.
(2) Click to download the search results in XLS form.
2. CRISPR

(1) Search input the gene ID, and the genome will be automatically identified laters.
Search to view the search results
3. Duplication type

(1) Enter the database and the corresponding gene ID.
Search to view the search results.
(2) Click to download the search results in XLS form.
4. Homologs
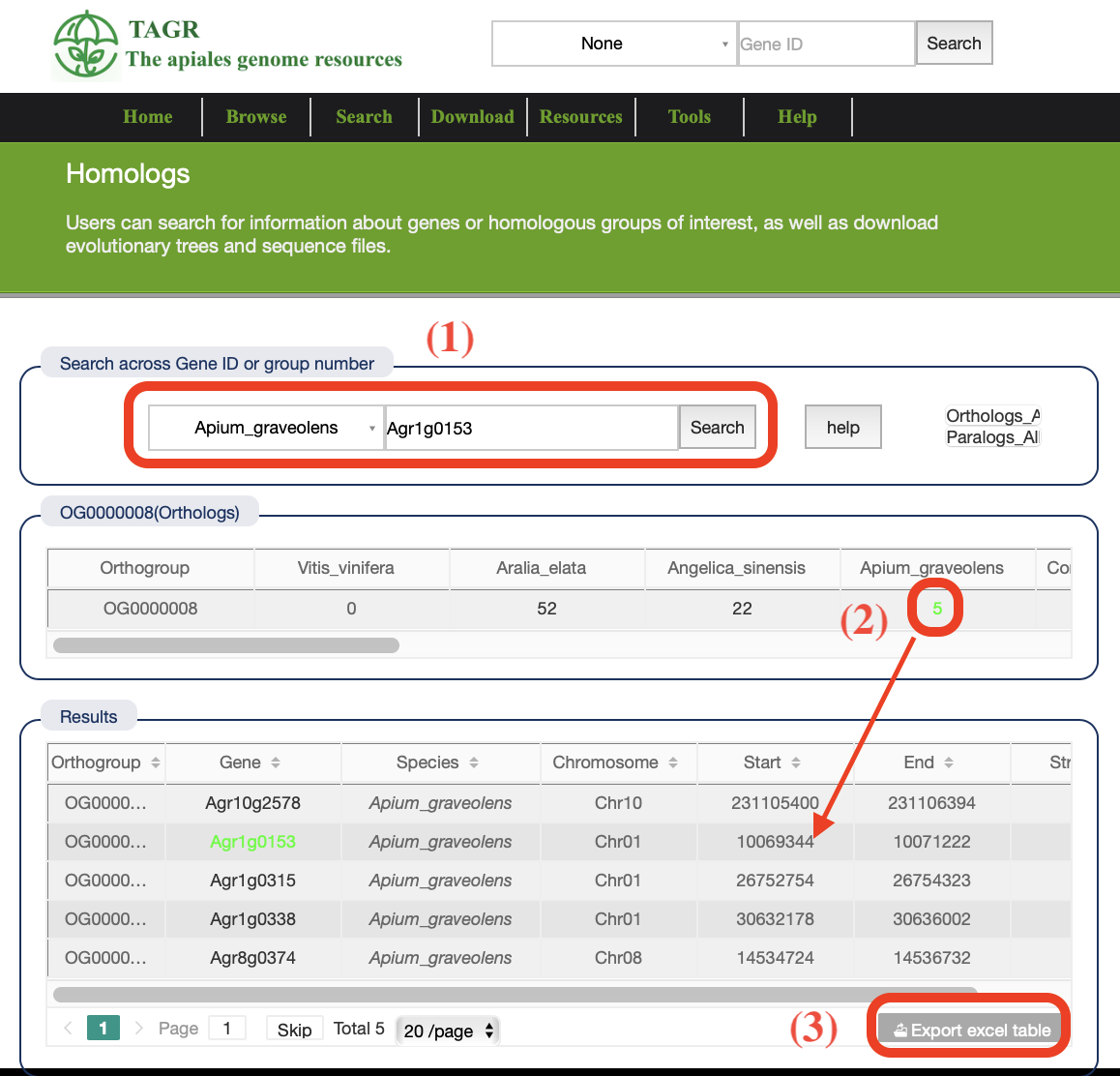
(1) Enter the gene ID, and the database will automatically identify which species and group the gene belongs to. You can see the group and specific information of this gene.
(2) Click on the number under each species to see the specific lineal homologous (or paragenetic homologous) genes.
(3) Click to download the search results in XLS form.
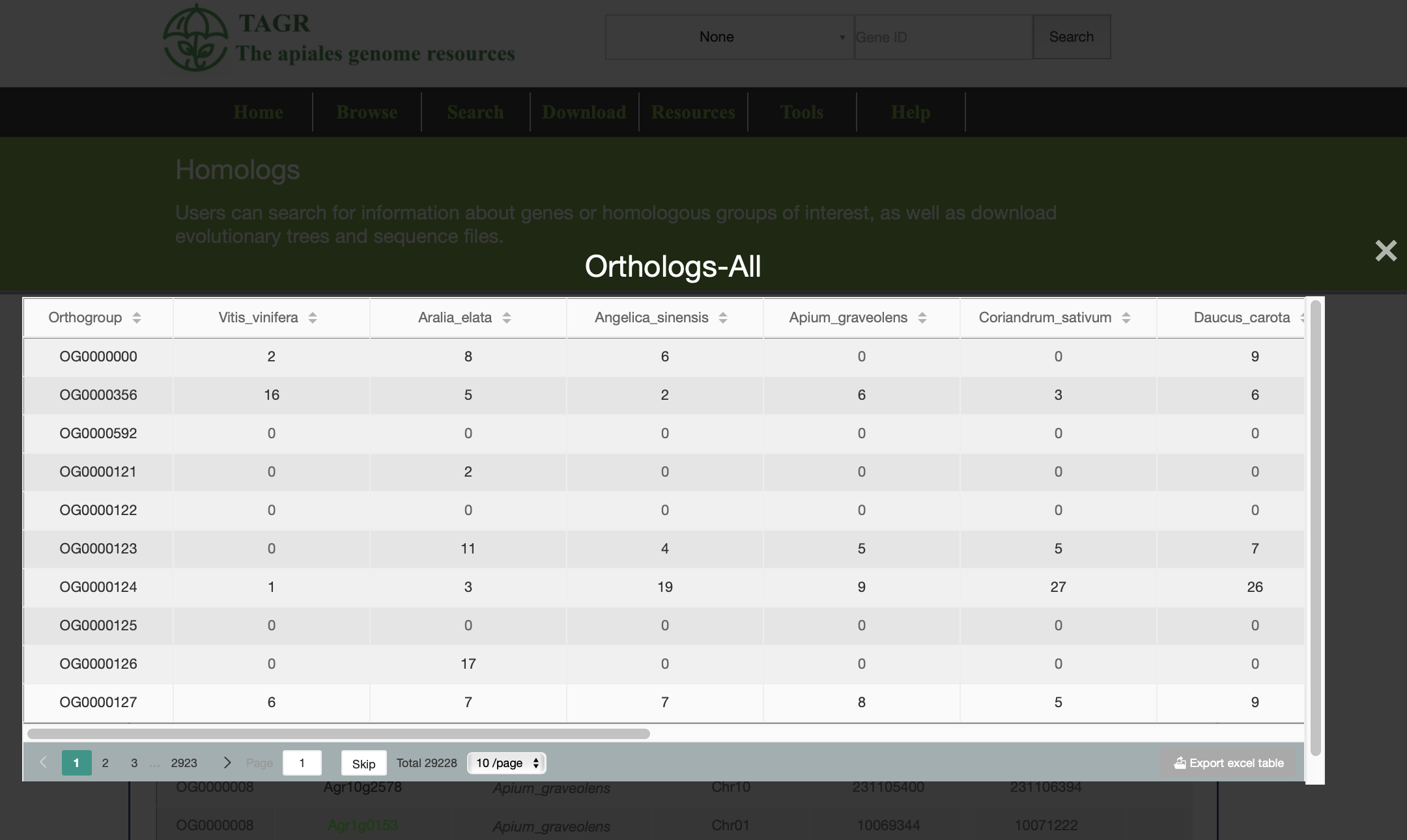
(1) Click on "orthologs_All" can view all the orthologous gene information of the group you search.
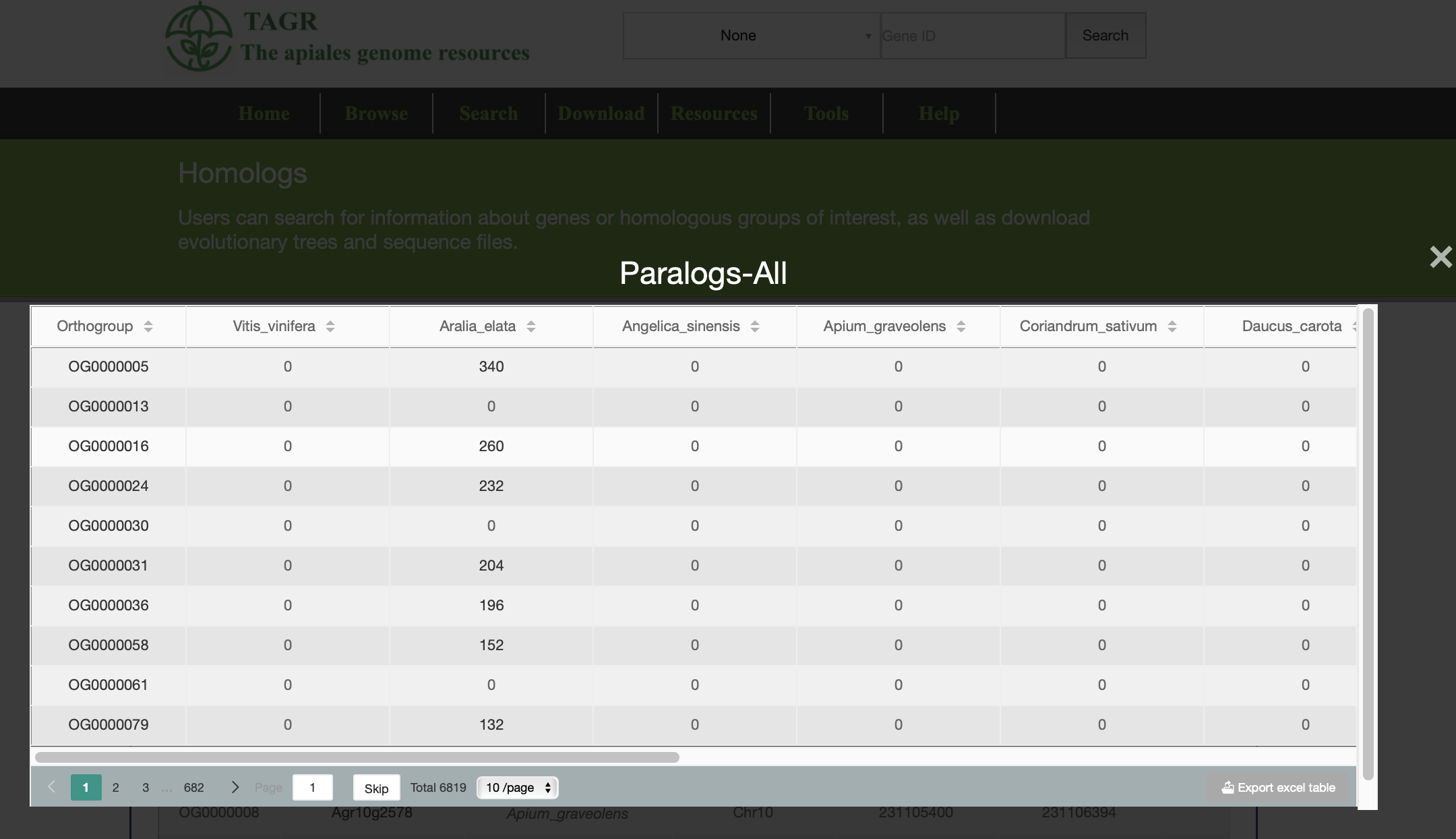
(1) Click "paralogs_All" can view all the collateral homologous gene information of the group you search.
5. Synteny
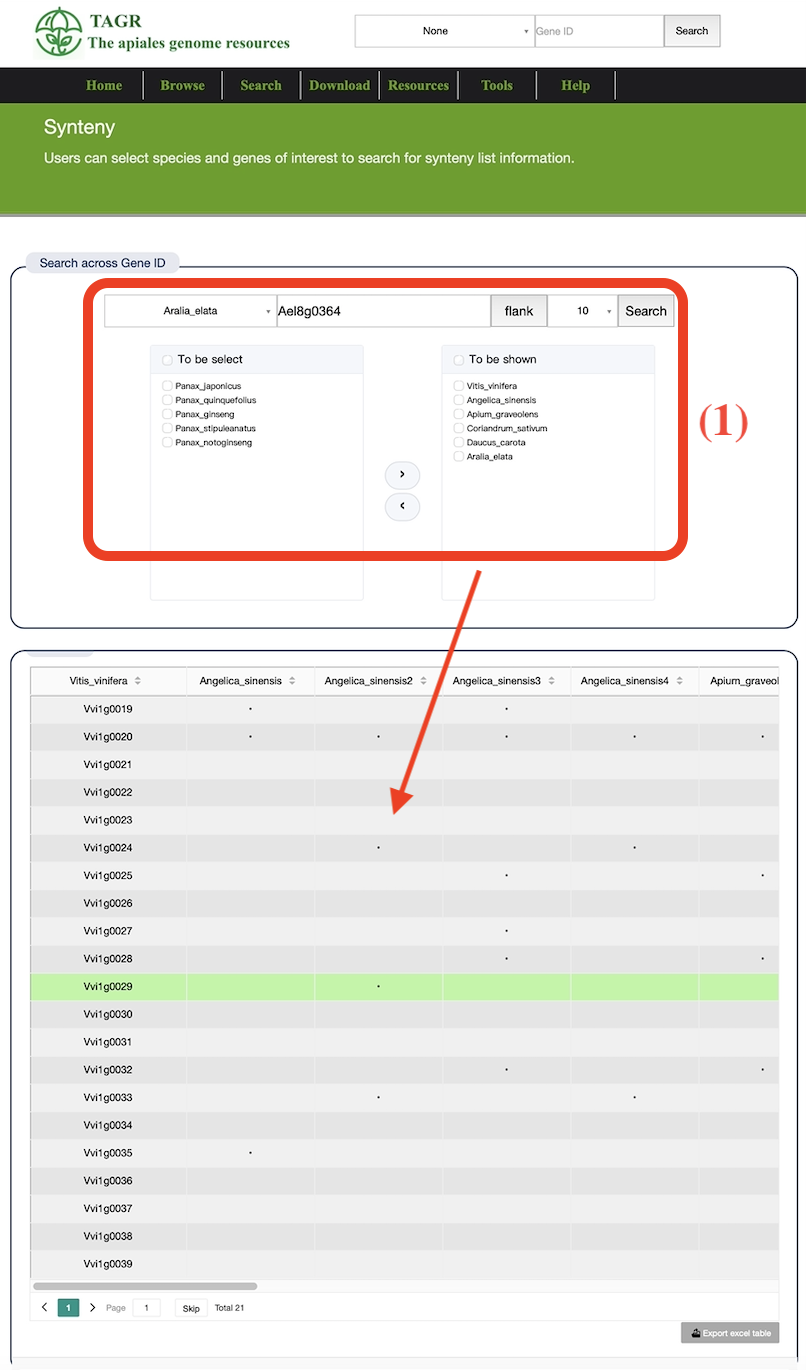
(1) Enter the corresponding gene ID, then select the number of flank and the genome of the species of interest.
(2) Searching can obtain the collinearity relationship between the searched gene species and the genome of interest.
(3) Each point represents a gene ID, which can be viewed by hovering the mouse.
6. RNA-Seq

(1) Select the genome and genes to search for, and then select different tissues for the search.
The search results are expression charts that can be used for log operations and downloads.

The download page contains some download files of 10 apiales plants and 2 model plants: genome files, CDS files, Protein files, GFF files, SSR files and publications.
1. Related database

This page shows some apiales plants related databases to provide users with more information.
2. Publication

This page contains the publications of 12 sequenced species.
1. Blast
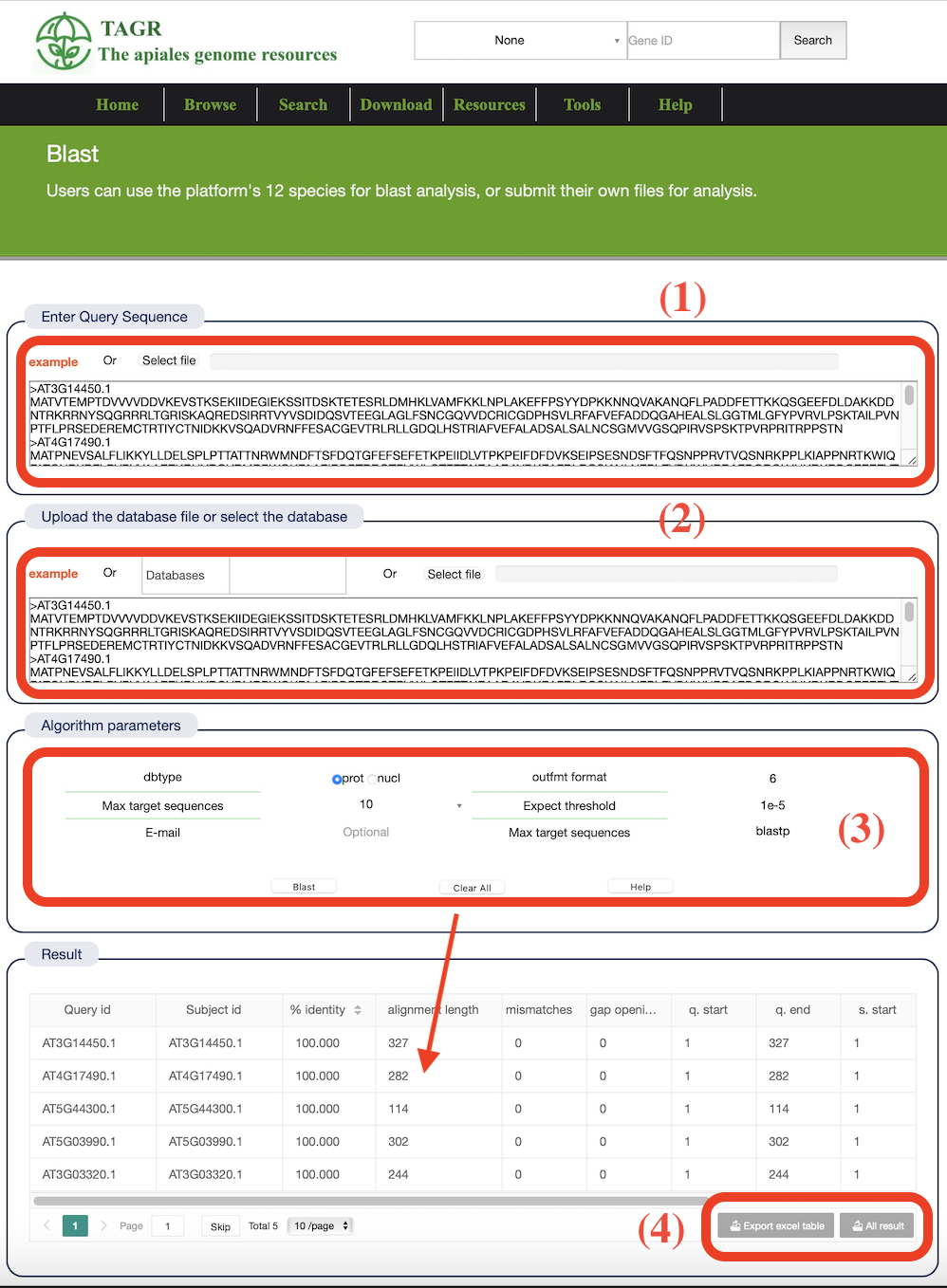
(1) Enter the FASTA sequence to be BLAST-aligned or submit the file.
(2) After successful operation, a history record will be generated. Click the link to view the results directly.
(3) Manually input the database creation file, submit the database creation file, or select a local database or multiple databases simultaneously.
(4) Select "dbtype", "out format", "Max target sequences", "Expect threshold", "Blast type". Enter an email to receive results.
(5) The BLAST result has 12 columns representing various alignment metrics.
The result will be sent to your mailbox later.
Note: the submitted file size should not exceed 200MB!
2. Synteny

(1) Choose two species of interest or submit the file.
(2) Search results can obtain collinearity maps between two species.
(3) Search results can obtain dotplot maps between two species.
(4) Click on the parts of interest in the collinearity maps and dotplot maps to view the information of collinearity gene pairs.
3. Primer

(1) Enter the fasta sequence that needs to be blast aligned or submit the file.
(2) Select the required parameters.
4. JBrowse

JBrowse page displays genome information such as genome version, assembly size, sequencing year, chromosomes number,etc.
(1) Click the more button to view the JBrowse interface of this species..
5. Hmmsearch
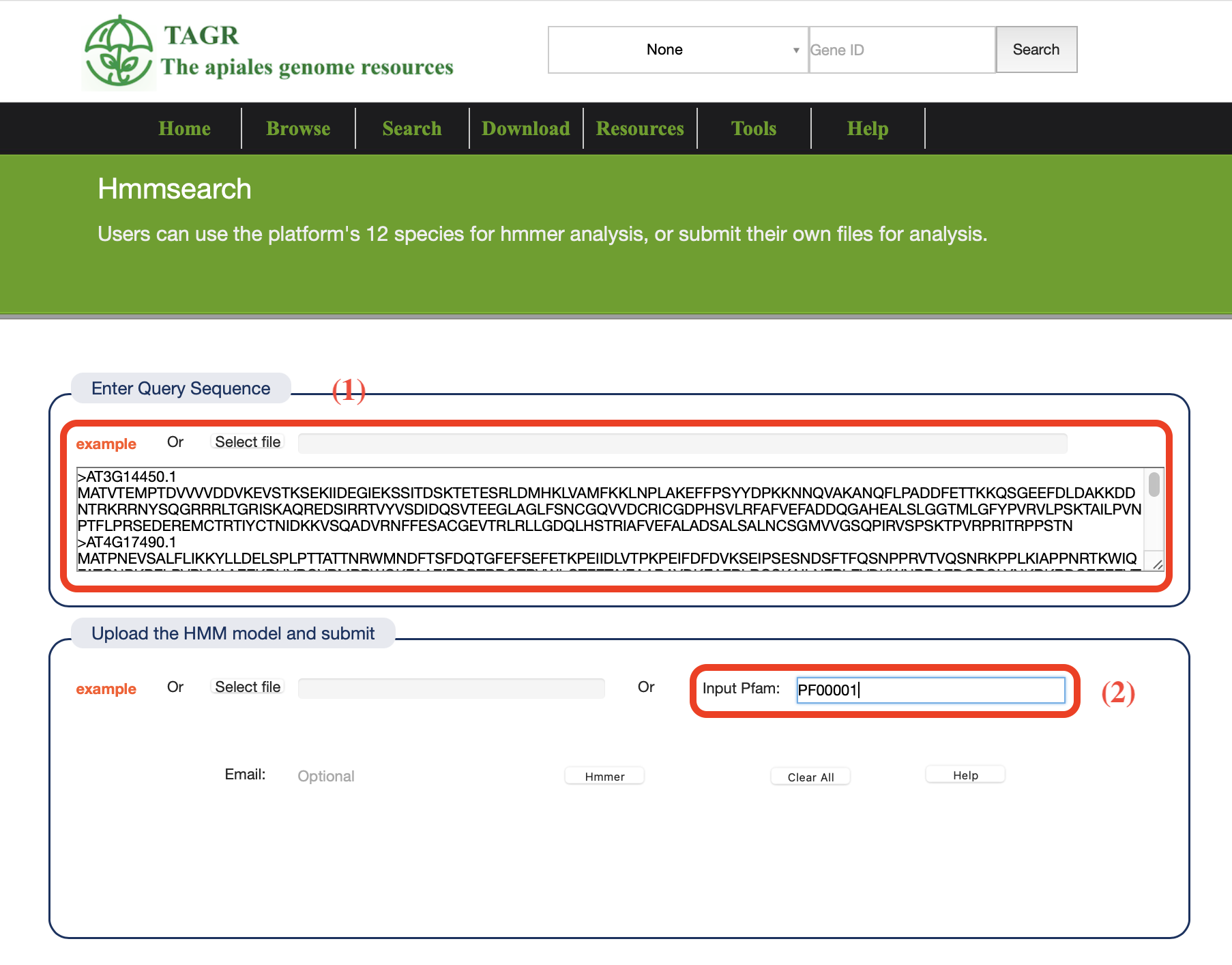
(1) Enter a example file or submit a sequence file.
(2) You can select online models or submit models yourself.
The results will be downloaded directly as files.
1. Functional annotation of genes
Gene annotations of 59 vegetable species were conducted using five protein databases, including Swiss-Prot and TrEMBL of UniProt knowledgebase( https://www.uniprot.org ),Pfam(v34.0)( http://pfam.xfam.org . Gene Ontology (go, http://geneontology.org )and non-redundant protein sequence database (NR, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov ). The annotation information of all genes was obtained by blastp with 59 vegetables with Arabidopsis thaliana.
2.Identification of orthologous, paralogous, and xenologous genes
OrthoFinder (v2.0) was used to identify orthologs, paralogs, and xenologs. First, the Blastp program was used to obtain the similarity relationships among the protein sequences in different species (E-value < 1e-5). Cluster analysis was then performed using the MCL algorithm (inflation value >1.5), and gene and species trees were built using each gene family of all species.
3.Detection of collinearity and duplication types
Collinearity analysis was performed by the Multiple Collinearity Scan toolkit (MCScanX) software with default parameters. First, Blastp was used to search for potential homologous genes (E-value < 10–5) among different species. Then, the collinearity was detected according to the Gff files and Blast results. Finally, collinear relationships were illustrated using TBtools. The duplicate_gene_classifier program from MCScanX was used to predict the duplication types.
4.Identification of TFs and functional genes
The 63 TF gene families were detected, using the Pfam database, from the protein sequences of 59 vegetable species (E-value < 1e-5). The 295 flowering genes of Arabidopsis were collected from previous studies and the FLOR-ID database. The 73 glucosinolate genes of Arabidopsis were collected from the previous reports, and the 41 anthocyanin genes and 151 auxin genes of Arabidopsis were obtained from the BRAD website. Homologous flowering, glucosinolate, anthocyanin, and auxin genes in other vegetable species were identified by Blastp (E-value < 1e-5; Identity >60%; Score >150) with manual checking.
5.Detection of resistance (R) genes
Three kinds of R genes were predominantly identified—nucleotide-binding site (NBS), receptor-like kinase (RLK), and receptor-like proteins (RLP) genes. The NBS genes of each species were detected by the accession number ‘PF00931’ in the Pfam annotation with an E-value < 1e-5. RLK genes were obtained from the Pfam annotation by the keyword ‘kinase’; in total, 15 gene families were assigned to the RLK genes. The 56 RLP genes of Arabidopsis were downloaded from the BRAD website, and homologous genes in other vegetable species were detected by Blastp program (E-value < 1e-5; Identity >60%; Score >150).
6.m6A identification
The m6A genes comprised three groups, including writers, readers (YTH), and erasers (AlkB). Writers had four gene families, including MTA70, WTAP, HAKAI, and VIRILIZER, which were identified by the accession numbers ‘PF05063’, ‘PF17098’, ‘PF18408’, and ‘PF15912’, respectively. The YTH genes of readers were detected by the accession number ‘PF04146’, and AlkB genes of erasers were detected by the accession number ‘PF13532 of the Pfam annotation..
7.Cas9 target sequence design for CRISPR
The CasFinder pipeline was used to design the Cas9 target sites for CRISPR. Firstly, the repetitive genome sequences were screened using the RepeatMasker program for each species. The index was then created for each genome by the Bowtie program. Finally, the scripts CasValue_v2.pl and CasFinder.pl from the CasFinder pipeline were adopted to design the guide sequences for the CRISPR study. The candidate sequence was filtered by in-house Perl scripts to obtain the specific sequence for each gene.
Telephone: 0315-8805607
Mail: songxiaoming116@163.com
Location: 21 Bohai Road, Caofeidian Xincheng, Tangshan 063210, Hebei, China
Working Hours:Mon - Fri: 8:00 am to 10:30 pm
Mail: songxiaoming116@163.com
Location: 21 Bohai Road, Caofeidian Xincheng, Tangshan 063210, Hebei, China
Working Hours:Mon - Fri: 8:00 am to 10:30 pm
Some pictures and data of this website come from the Internet and other public database platforms. Copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact Song Xiaoming (songxiaoming116@163.com) in time to delete it. In addition, all data in this database is free for all scientists to use. For commercial use, please contact us for authorization.